TMS Therapy for
Insomnia: A Non-Invasive Treatment Option
Struggling with insomnia can affect every part of daily life, from focus and mood to overall health, leaving many patients frustrated after medications or behavioral therapies fail to provide lasting relief. TMS therapy offers a non-invasive, drug-free option for individuals concerned about chronic sleeplessness, medication side effects, dependency, or insomnia linked to underlying mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety. By gently stimulating targeted brain regions involved in sleep regulation, TMS therapy may help restore healthier sleep patterns and improve overall well-being.
Our online directory makes it easy to explore this innovative treatment by connecting patients with qualified TMS providers in their region, helping you find care that’s accessible, personalized, and close to home.
TMS Therapy for Insomnia: A Non-Invasive Treatment Option
Struggling with insomnia can affect every part of daily life, from focus and mood to overall health, leaving many patients frustrated after medications or behavioral therapies fail to provide lasting relief. TMS therapy offers a non-invasive, drug-free option for individuals concerned about chronic sleeplessness, medication side effects, dependency, or insomnia linked to underlying mental health conditions, such as depression or anxiety. By gently stimulating targeted brain regions involved in sleep regulation, TMS therapy may help restore healthier sleep patterns and improve overall well-being.
Our online directory makes it easy to explore this innovative treatment by connecting patients with qualified TMS providers in their region, helping you find care that’s accessible, personalized, and close to home.

What Is TMS Therapy?
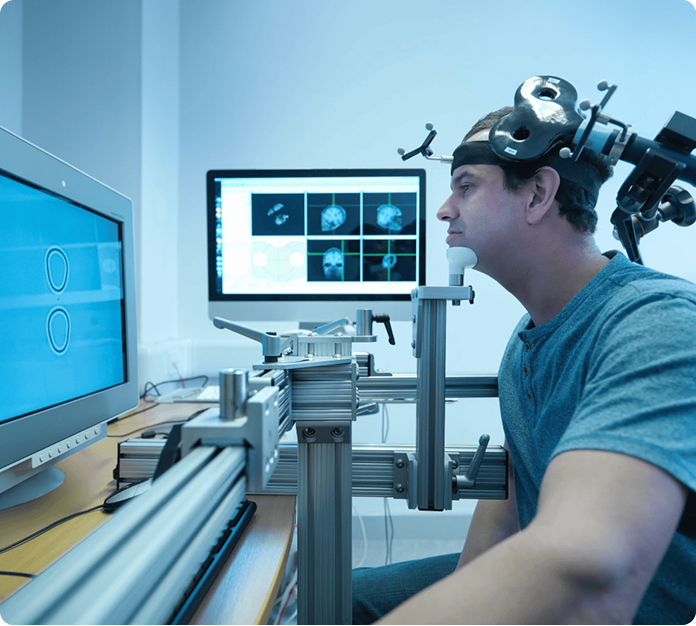
Is TMS Effective for Insomnia Treatment?
TMS for Insomnia: A Step-by-Step Procedure
Initial Consultation
Brain Mapping
Treatment Sessions
Treatment Schedule
Ongoing Monitoring

Recovery & Side Effects
Recovery after TMS therapy for insomnia is minimal, as the procedure is non-invasive and does not involve anesthesia or sedation. Most patients can resume normal daily activities immediately after each session, including work or school. Side effects are generally mild and temporary, with the most common being scalp discomfort, tingling sensations at the treatment site, or a mild headache during or shortly after sessions. These effects typically lessen as treatment progresses and can be managed by adjusting stimulation settings as needed. Serious side effects are rare, and providers closely monitor patients throughout treatment to ensure comfort and safety.
Candidates for TMS Therapy
for Insomnia

Benefits of TMS Therapy for Insomnia
- Non-invasive, outpatient treatment with no anesthesia required
- Drug-free option for patients concerned about long-term use of sleep medications
- Targets brain activity patterns that contribute to chronic insomnia
-
Minimal downtime, allowing patients to resume daily
activities immediately - May improve sleep onset, sleep maintenance, and overall sleep quality
- Generally well-tolerated with mild, temporary side effects
Cost of TMS Therapy for
Insomnia in the U.S.
