Find the
Best TMS Therapy
Near Me
Most Insurance Accepted
Insurance May Cover Up to 100%
Top Rated TMS Clinics Near
How Do I Get Started?

Find a Provider
Enter your address or postal
code on this page to find
providers near you.

Book your appointment

Meet with your TMS provider
Find Out If You’re a Candidate
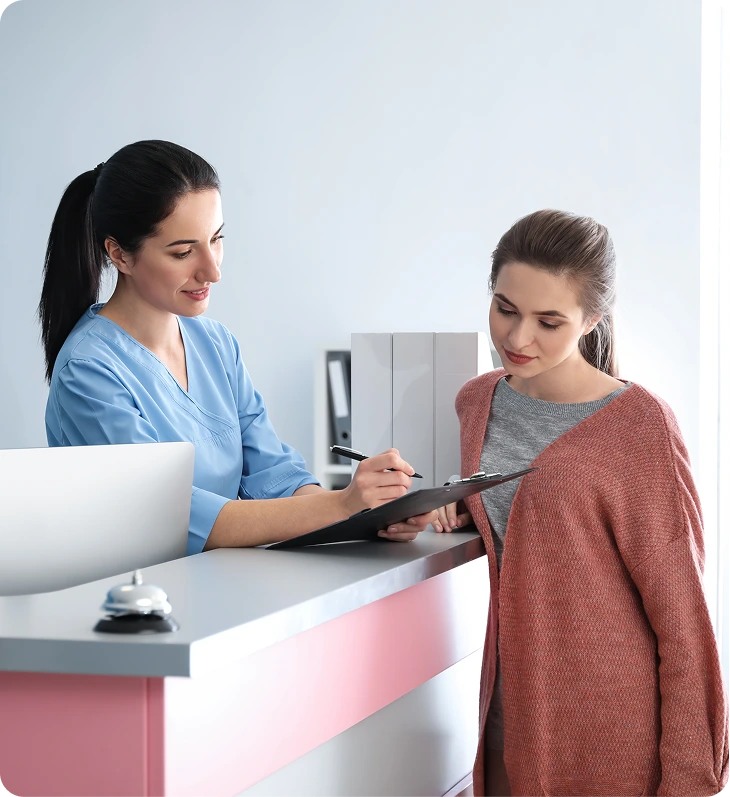

They help you explore whether treatments like TMS, Spravato, or Ketamine therapy may be the best fit, or if other options could support your needs. These quizzes are not a replacement for medical advice, but they give you clarity before meeting with your provider.
- Simple questions that highlight your treatment options
- Guidance to see if the therapy you’re considering is the right match
- Support in preparing for your consultation with a licensed provider
A quick quiz can be the first step toward the right care for you.

What is TMS Therapy?
Why People with Treatment-Resistant Depression Choose TMS therapy

Conditions TMS Therapy Can Cure
About TMS Therapy
TMS Therapy Most Common Questions
Is TMS FDA approved?
Yes, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is FDA-approved. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved TMS therapy for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in patients who have not responded to traditional treatments such as antidepressant medications.
What happens during a TMS procedure?
During a Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) procedure, the following steps typically occur:
- Preparation: The patient sits comfortably and wears earplugs to protect against the TMS device’s clicking sound.
- Positioning: An electromagnetic coil is placed against the patient’s scalp, usually targeting the left prefrontal cortex.
- Mapping: The provider may perform a mapping session with test pulses to identify the precise stimulation spot.
- Stimulation: The TMS machine generates magnetic pulses that create electrical currents, stimulating nerve cells in the brain. The patient hears clicking and feels tapping on the scalp.
Who administers TMS?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is typically administered by a trained healthcare professional, such as: –
- Psychiatrists: Medical doctors specializing in mental health, often oversee TMS treatments, especially since it is commonly used for treating depression.
- Neurologists: Medical doctors specializing in disorders of the nervous system may also administer TMS, particularly if it is used for conditions beyond depression.
- Trained Technicians: Under the supervision of a psychiatrist or neurologist, certified TMS technicians or other trained medical staff can administer the actual sessions.
Do I need to be hospitalized for a course of TMS?
No, you do not need to be hospitalized for a course of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). TMS is an outpatient procedure, meaning you can visit the clinic for each session and go home immediately afterward.
What are the side-effects of TMS?
The side effects of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) are generally mild and temporary. Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Scalp Discomfort
- Lightheadedness
- Facial Muscle Twitching
- Hearing Discomfort
Is TMS Therapy covered by insurance?
Yes, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy is often covered by insurance, but coverage can vary depending on the insurance provider and the specific policy.
Is TMS FDA approved?
Yes, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is FDA-approved. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) has approved TMS therapy for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in patients who have not responded to traditional treatments such as antidepressant medications.
What happens during a TMS procedure?
- During a Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) procedure, the following steps typically occur:
- Preparation: The patient sits comfortably and wears earplugs to protect against the TMS device’s clicking sound. – Positioning: An electromagnetic coil is placed against the patient’s scalp, usually targeting the left prefrontal cortex. – Mapping: The provider may perform a mapping session with test pulses to identify the precise stimulation spot. – Stimulation: The TMS machine generates magnetic pulses that create electrical currents, stimulating nerve cells in the brain. The patient hears clicking and feels tapping on the scalp.
Who administers TMS?
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is typically administered by a trained healthcare professional, such as:
- Psychiatrists: Medical doctors specializing in mental health, often oversee TMS treatments, especially since it is commonly used for treating depression.
- Neurologists: Medical doctors specializing in disorders of the nervous system may also administer TMS, particularly if it is used for conditions beyond depression.
- Trained Technicians: Under the supervision of a psychiatrist or neurologist, certified TMS technicians or other trained medical staff can administer the actual sessions.
Do I need to be hospitalized for a course of TMS?
No, you do not need to be hospitalized for a course of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS). TMS is an outpatient procedure, meaning you can visit the clinic for each session and go home immediately afterward.
What are the side-effects of TMS?
The side effects of Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) are generally mild and temporary. Common side effects include:
- Headache
- Scalp Discomfort
- Lightheadedness
- Facial Muscle Twitching
- Hearing Discomfort
Is TMS Therapy covered by insurance?
Yes, Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) therapy is often covered by insurance, but coverage can vary depending on the insurance provider and the specific policy.



