The evolution of therapeutic approaches has brought us from the controversial methods of the past to more refined and safer solutions of the present. Two treatments that often draw comparisons are electroconvulsive therapy (ECT), commonly known as “shock therapy,” and transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS). While both procedures aim to alleviate severe conditions like depression, their methods, side effects, and patient experiences differ significantly. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for anyone navigating treatment options in the modern mental health landscape.
Shock Therapy vs TMS Therapy
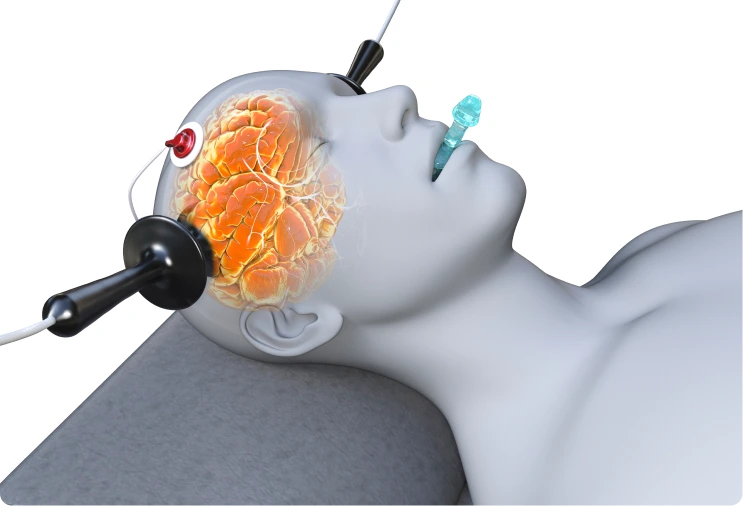
The time commitment and schedule for each therapy differs substantially in addressing depression symptoms. ECT typically requires 6-12 treatments over 2-4 weeks, with each session demanding several hours when accounting for preparation, the procedure, and recovery from anesthesia. TMS follows a more intensive but manageable schedule, usually involving 20-30 visits during 4-6 weeks. Each treatment lasts about 30-40 minutes, allowing patients to easily integrate the therapy into their daily routines and return immediately to normal activities. There are also accelerated TMS protocols that include shorter sessions (3-10 minutes) and can be completed more quickly.
The speed of response and effectiveness vary between the two procedures. ECT often produces rapid results, with some patients experiencing significant improvement within 6-12 sessions, making it particularly valuable in crises where immediate intervention is necessary. TMS typically requires more procedures to achieve full benefits, with improvements usually becoming noticeable after 2-3 weeks. Like talk therapy, it often works best as part of a comprehensive treatment approach. The overall success rates are slightly higher for ECT. However, practice shows that more than 50% of TMS patients respond to procedures, and nearly 30% achieve remission.
Electrical currents induce a controlled seizure
Magnetic pulses stimulate specific brain regions
Invasive (requires anesthesia and medical monitoring)
Noninvasive (performed while the patient is awake)
Memory loss, confusion, headaches, muscle aches, nausea
Mild scalp discomfort, temporary headaches, minor muscle twitches
6-12 sessions over 2-4 weeks, requiring hours per procedure
20-50 sessions over 1-6 weeks, lasting 3-40 minutes each
Generalized effect on broad brain regions
Precise stimulation of mood-regulating areas (e.g., dorsolateral prefrontal cortex)
Severe cases (e.g., treatment-resistant depression, suicidal tendencies)
Moderate to severe depression or OCD unresponsive to medication
Yes, requires general anesthesia and muscle relaxants
No anesthesia or sedation is required
Several hours due to anesthesia; potential memory issues
No downtime; patients resume daily activities immediately
Rapid results after a few sessions
Gradual improvement, typically noticeable after 2-3 weeks
Higher upfront cost due to medical facility fees; widely covered by insurance
Covered for FDA-approved applications after failing 1-4 medications
